Throat : Larynx, Hypopharynx Cancer
Signs and Symptoms of Throat Cancer
- Pharynx – The pharynx is a hollow tube about 5 inches long that starts behind the nose and leads to the esophagus (food pipe ) and the trachea (wind pipe). The pharynx has three parts
- Nasopharynx – The nasopharynx, the upper part of the pharynx, is behind the nose.
- Oropharynx – The oropharynx is the middle part of the pharynx. The oropharynx includes the soft palate (the back of the mouth), the base of the tongue, and the tonsils.
- Hypopharynx – The hypopharynx is the lower part of the pharynx.
- Larynx – The larynx, also called the voice box, is a short passageway formed by cartilage just below the pharynx in the neck. The larynx contains the vocal cords. It also has a small piece of tissue, called the epiglottis, which moves to cover the larynx to prevent food from entering the air passages.
Most Common Symptoms
- Hoarseness of voice
- Swelling or lump in the neck
- Ear pain
- Difficulty in swallowing (more to solid food)
- Difficulty in breathing
- Persistent cough
Types of Cancer
Cancer of throat means involvement of hollow tube from behind nose to top of windpipe. It means nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx and larynx(voice box )
Causes and Risk Factors of Throat Cancer

Smoking-most important

Alcoholism

Viral infections—HPV,EBV

Iron/ nutritional deficiency

Reflux oesophagitis
Screening and Diagnosis
Heavy smoker should have regular check ups. Be aware of early warning signals of head and neck cancers.If symptoms don’t subside in 3 week’s time , report to the doctor for clinical examination and further investigations.
How Do We Diagnose?
To find the cause of symptoms, a surgical oncologist evaluates a person’s medical history, performs a physical examination, and orders diagnostic tests. The examination and tests conducted may vary depending on the symptoms. Direct Laryngoscopy is done to view the larynx and take a biopsy;
- Laboratory tests examine samples of blood, urine, or cells from the nodes.
- CT scan /Magnetic resonance imaging (or MRI) of head and neck.
- PET scan in selected advanced cases..
Treatment of Throat Cancer
Surgeries Offered
- Microlaryngeal surgery(MLS)
- LASER cordectomy
- TORS(Trans Oral Robotic Surgery)
- Total laryngectomy
- Partial laryngectomy
- Gastric pull-up with total laryngopharyngoesophagectomy
- Reconstruction of neopharynx with Free Flaps and regional flaps.
Discuss details of surgery with your surgeon. do ask about consequences and complications of surgery.
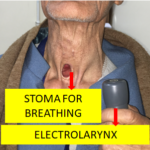
Cancer of larynx (voice box)operated. He uses electrolarynx for speaking. He eats through his mouth.
DO’s after Surgery
- Liquid diet with adequate salt has to be given at regular intervals of 2 hours through a feeding bag and tube.
- Feeding through tube should be given with patient in sitting or 30degree head-up position. Each feed of around 300 ml should be given slowly over a period of 20 minutes.
- All medicines as prescribed in the discharge note along with medicines for chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, thyroid-related, and asthma should be continued as earlier.
- You can brush your teeth. Oral hygiene with Betadine mouth wash in 1:1 ratio with water every 6 hours.
- Walking and moving around is a must.
- If tracheostomy tube is there, you may have to clean the inner cannula frequently preferably every 2-3 hourly. Learn tracheostomy care from doctor or nurse at the time of discharge from hospital.
- Walking and moving around is a must.
- If the tracheostomy tube is there you may have to clean the inner cannula frequently preferably every 2-3 hourly.
- Keep the bib wet around the tracheostomy tube or stoma.
- Keep the cuff of the tracheostomy tube deflated. If advised for inflation, you can inflate with 5 ml air.
- Shoulder exercises as and when advised.
- Minimal blood-stained discharge from tracheostomy tube secretions is considered normal, don’t panic.
- Care of the drain and output charting as advised (you can see the video attached for reference).
- Care of the wound as advised.
- Care of the stoma: cleaning with saline spray adequately around it. Some amount of spray may trickle inside the stoma leading to coughing, it’s normal, don’t panic. Remove any discharge or sputum near the stoma with a gauze piece.
DON'Ts after Surgery
- Taking bath without caring for stoma.
- Use of room heaters.
- Continue addictions.
- Using cotton for cleaning or wound dressing near the stoma. It may accidentally enter the lungs.
- Swimming.
Clinical Trials of Throat Cancer
Tumor Board/ Multispecialty Clinic Evaluation
Each and every Head & Neck cancer patient is evaluated by a special team of Surgical Oncologists (Head & Neck unit), Medical Oncologists, Radiation Oncologists, Onco-pathologists and Imaging Specialists. Depending on the age, general condition, type of pathology and stage of the disease, a custom made treatment plan is charted out for each and every patient as per International Treatment Guidelines. (NCCN – National Comprehensive Cancer Network)
When to Reach the Treating Team?
- As per appointment.
- If the swelling around the neck wound increases suddenly or within few hours.
- Fresh bleeding from neck wound or oral cavity or stoma. Minimal blood-stained discharge during coughing is acceptable.
- If there’s difficulty in breathing or swallowing, fever.
- If symptoms of hypocalcemia appear (tingling, numbness, or twitching sensation around lips, finger tips, and toe tips. Spasm of hands and feet). Immediately have 4 tablets of calcium. The required injection of Calcium Gluconate is written in your discharge summary. You can receive the same at any nearest health care institution.